|
英国 United Kingdom 爱尔兰 Ireland 比利时 Belgium 荷兰 Netherlands 法国 France 西班牙 Spain 葡萄牙 Portugal 意大利 Italy 希腊 Greece 奥地利 Austria 匈牙利 Hungary 德国 Germany 瑞士 Switzerland 罗马尼亚 Romania 俄罗斯 Russia 波兰 Poland 克罗地亚 Croatia (Hrvatska) 捷克 Czech 芬兰 Finland 瑞典 Sweden 挪威 Norway 冰岛 Iceland 土耳其 Turkey 丹麦 Denmark 阿尔巴尼亚 Albania 爱沙尼亚 Republic of Estonia 安道尔 Andorra 白俄罗斯 Belarus 保加利亚 The Republic of Bulgaria 波斯尼亚和黑塞哥维那 Bosnia and Herzegovina 梵蒂冈 Vatican City State (Holy See) 黑山 The Republic of Montenegro 拉脱维亚 Latvia 立陶宛 Republic of Lithuania 列支敦士登 Liechtenstein 卢森堡 Luxembourg 马耳他 Republic of Malta 马其顿 The Republic of Macedonia 摩尔多瓦 The Republic of Moldova 摩纳哥 Monaco 塞尔维亚 the Republic of Serbia 斯洛伐克 The Slovak Republic 斯洛文尼亚 the Republic of Slovenia 圣马力诺 San Marino 乌克兰 Ukraine |
| Croatia (Hrvatska) Capital:Zagreb Country Code: hr |
|
克罗地亚共和国(The Republic of Croatia)。即“赫尔瓦次卡”。
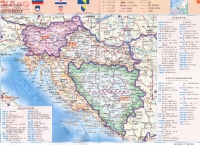
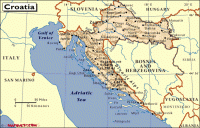
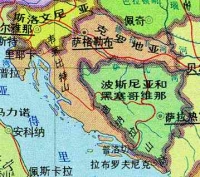
国旗 克罗地亚国旗呈长方形,长与宽之比约为3∶2。由三个平行相等的横长方形组成,自上而下分别为红、白、蓝三色。旗面中间绘有国徽。克罗地亚于1991年6月25日宣布脱离原南斯拉夫独立,上述新国旗是1990年12月22日开始启用的。 国徽 克罗地亚国徽为盾徽。盾面由25个红、白相间的方格组成。盾徽上端有一个风格化的王冠,王冠由五个小盾组成。从左至右五个小盾上的图案分别为:一弯白色新月和一枚黄色六角星;蓝、红相间的条带;三个饰有王冠的黄色狮子头;红角红蹄的山羊;一只貂和一颗六角星。国徽来自9世纪的克罗地亚古老王国的标志,五个小盾象征当时王国的五个省区。 国家政要 总统斯捷潘·梅西奇(Stjepan Mesic),2000年2月当选总统。2005年1月蝉联总统。 自然地理 面积56538平方公里。克罗地亚位于中欧的东南边缘,巴尔干半岛的西北,亚得里亚海东岸。隔亚得里亚海与意大利相望,北部得邻国是斯洛文尼亚和匈牙利,东面和南面则是塞尔维亚与波黑。西南部为迪纳拉山地,多岩溶地貌。沿海为达尔马提亚海岸,北部为斯拉沃尼丘陵与萨瓦河沿岸平原。沿海为地中海式气候,内陆逐渐向温带大陆性气候过渡。农业集中在沿萨瓦河两岸的平原地区,农产品有甜菜、玉米、小麦、烟草、葡萄等。沿海产油橄榄、柠檬、柑橘等亚热带果类。山地丘陵区畜牧业发达。有煤、石油、天然气、铝土矿等开采。该国岛屿众多,大、小共1185个,由此克罗地亚也被很多人成为“千岛之国”。特殊的地理使克罗地亚境内呈现两种不同的气候类型,沿海地区为地中海式气候,内陆地区则是四季分明的大陆性气候。克罗地亚分为3个地理区域:北部、东北部平原,中部山地,伊斯特拉半岛和达尔马提亚沿海地区。 人口 4,282,216 (2000年7月)。主要民族是克罗地亚族(78.1%),其他为塞尔维亚族、穆斯林族、匈牙利族、意大利族、阿尔巴尼亚族、捷克族等。官方语言为克罗地亚语。主要宗教是天主教(信教人数占总人口的76.6%)。 克罗地亚海港城市杜布罗夫尼克位于亚得里亚海滨,是克罗地亚著名的旅游中心和疗养胜地。这里依山傍海,风景优美,气候温和,被誉为“亚得里亚海明珠”和“城市博物馆”。城区分旧城和新城两部分。杜布罗夫尼克不仅是欧洲中世纪建筑保存较完好的一个城市,而且也是一座文化城市,每年都要举办一次”杜布罗夫尼克之夏”戏剧节。在克罗地亚境外的邻国,以及美国,澳大利亚等地区还居住着约400万的克罗地亚人。 宗教 居民多信奉天主教和东正教 货 币 第纳尔 首都 萨格勒布 Zagreb位于克罗地亚的西北部,坐落在萨瓦河西岸,梅德韦德尼察山脚下。面积284平方公里。人口77万(2001年)。一月平均气温-1.6℃,七月平均气温20.9℃,年平均气温12.7℃。年平均降水量890毫米。 重要城市 奥西耶克,位于东部的平原地区,克罗地亚的粮仓 瓦拉日丁,位于北部,宿有巴洛克之城的美誉 里耶卡,位于西北,拥有克罗地亚的第一大港口,里耶卡港在罗马帝国时期,还曾一度是欧洲最大的港口 杜布罗夫尼克,位于最南端,被称为亚得里亚海上的珍珠。在巴尔干地区被不同异族统治了上千年的同时,杜布罗夫尼克却一直作为独立的共和国存在,直至被拿破仑所占领。 节日 新年(1月1日) 劳动节(5月1日) 建军节(5月28日) 国庆( 5月30日) 反法西斯战争胜利日(6月22日) 感恩节 (8月5日) 万圣节 (11月1日) 圣诞节(12月25日) 二、简史 6世纪末7世纪初,斯拉夫人移居到巴尔干半岛定居。8世纪末和9世纪初,克罗地亚人建立了早期封建国家。10世纪建立了强盛的克罗地亚王国。1102至1527年处于匈牙利王国统治之下。1527至1918年受哈布斯堡王朝的统治,直至奥匈帝国崩溃。1918年12月,克罗地亚与一些南部斯拉夫民族联合成立塞尔维亚-克罗地亚-斯洛文尼亚王国,1929年改称南斯拉夫王国。1941年,德意法西斯入侵南斯拉夫,建立了“克罗地亚独立国”。1945年反法西斯胜利后,克罗地亚与南斯拉夫合并。1963年改称南斯拉夫社会主义联邦共和国,克成为六个共和国之一。1990年5月,克举行二战后首次多党制大选,克民主共同体获胜执政。同年12月,克通过新宪法,规定克为主权和民主国家。1991年6月25日,克罗地亚共和国宣布独立,同年10月8日正式宣布脱离南斯拉夫联邦共和国。此举引起克境内塞尔维亚居民的武装抵抗。1992年2月,联合国安理会通过决议,决定向克境内的塞尔维亚族聚居区派遣联合国保护部队。克罗地亚为北约伙伴国 ,目前正在积极加入北约。 1992年5月22日,克罗地亚加入联合国。 三、经济 森林和水力资源丰富,全国森林面积207.9万公顷,森林覆盖率为43.5%。此外,还有石油、天然气、铝等资源。主要工业部门有食品加工、纺织、造船、建筑、电力、石化、冶金、机械制造和木材加工业等。克旅游业发达,是国民经济的重要组成部分和外汇收入的主要来源。主要风景区有秀丽迷人的亚得里亚海海滨、普利特维采湖群和布里俄尼岛等国家公园。 重要港市有奥西耶克、里耶卡、斯普利特、普拉等。 克罗地亚历史名城斯普利特市的戴克里先宫。建于公元305年的戴克里先宫,占地3万平方米,宫殿墙高17—21米,宽2米,正门6根大理石柱是远涉重洋从中东运来的,工程浩繁,宏伟壮丽。1979年,戴克里先宫被列入联合国教科文组织的《世界遗产名录》。 四、文化 克罗地亚有众多博物馆,其中相当一部分是归私人所有的;克罗地亚国家剧院的历史可追溯到1868年。演出的水平很高超,而票价却很低廉,平民很容易接触到高雅艺术。 发明 领带,在克罗地亚语中,克罗地亚的民族名称与领带这个词还极为相似。克罗地亚人是hrvata,而领带是kravata。 钢笔,发明者的姓氏是Penkala,中文译为彭卡拉。英文中的钢笔叫做pen,这大概就是取的发明者Penkala姓氏中的第一个音节而来的。 新闻出版 1996年,克共有1760家出版单位,出版刊物约3000种。克文全国性报刊共有两种:《晚报》,日发行量205000份;《信使报》42000份;地方性日报共有九种:如《自由达尔马提亚报》120000份;《新报》4000份等。 除克国家电视台(HTV)外,全国目前有7家省市级商业电视台。另外,克全国现有电台108家,其中国家级3家、省级12家和市级93家。 克目前拥有4家通讯社,包括克罗地亚通讯社(HINA)、克通社影像社(FaH)、天主教信息通讯社(IKA)和斯普利特私人新闻通讯社(STINA)。其中克通讯社为国家通讯社,成立于1990年7月。 五、外交 重视发展同大国的友好合作关系;在坚决维护国家利益和平等互利的基础上,同所有国家发展政治、经济、文化等领域的全面关系、融入欧洲经济安全一体化,重视加强同中欧和邻国的关系。 与中国关系 1992年4月27日,中国承认克罗地亚共和国,同年5月13日,中克两国建交。2005年5月,克罗地亚总理萨纳德来华正式访问,两国签署建立全面合作伙伴关系的联合声明。 六、运动 克罗地亚的队伍也多次取得过水球,手球的世界冠军。 克罗地亚国内有足球俱乐部联盟比赛。萨格勒布的迪那摩和斯普立特的海杜克是闻名于欧洲的俱乐部。在1998年法国世界杯上,克罗地亚足球队黑马一般,取得了第三名的成绩。 克罗地亚队是前南斯拉夫足球的重要力量,他们依靠自己民族特有的天才与勤奋创造了足球史上的无数经典。其国家独立后,该国足球队在世界杯和欧锦赛上的成绩可圈可点,其中,1998年,克罗地亚队第一次参加世界杯便取得了季军的好成绩,苏克还成为了最佳射手。克罗地亚队的球衣也是其国旗的色彩,红白格的经典队服在国际足坛独树一帜。 篮球方面,南斯拉夫地区的篮球运动曾经被西方媒体称作除NBA之外,最受人关注的篮球比赛。乒乓球方面,克罗地亚有着良好的传统。运动员水平在欧洲属于很高的。 不乏出色的网球选手,伊万·柳比西奇是克罗地亚的网球明星,曾经可以与费德勒抗衡,他还战胜过阿加西。戈兰·伊万尼塞维奇,在2001年的温布尔登网球锦标赛中共发出多达227个Ace球,并以外卡球员身份夺得该届男单冠军。2004年他宣布退役,但2005年曾一度复出,并以替补身份协助克罗地亚争夺戴维斯杯锦标,结果克罗地亚如愿首夺该项标。 七、历史人物 马可·波罗,他出生于克罗地亚的考尔楚拉岛。该地区当时受到威尼斯这个国家的统治。又由于他的游记是用当时的意大利语写成的,所以世人才多称他为威尼斯人,或意大利人。 尼古拉·特斯拉,这为克罗地亚科学家在青少年时期就有很多发明创造,到美国工作后他作出了巨大的贡献 ―― 发明了交流电 ,在科学技术的发展史上,特斯拉被称为人类进入电气时代的重要推动者。 墨霍罗维奇,著名地质学家,一个地层以他的名字命名 马克西姆 (Maksim)于1975年生于克罗埃西亚的雅德里亚海岸、一个叫做ibenik的小镇,九岁开始学习钢琴,随即展现他在钢琴演奏上过人的天赋。(1999年)赢得鲁宾斯坦钢琴大赛首奖。 现为欧洲新古典王子、钢琴圣手。 Croatia is a member of United Nations, the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe and the Council of Europe. The country is also a candidate for membership of the European Union and received a NATO membership invitation on 3 April 2008. On October 17, 2007 Croatia became a non-permanent member of the United Nations Security Council for the 2008-2009 term. The Croats settled on the east coast of the Adriatic Sea and the Pannonian lands in early 7th century, forming two principalities, Dalmatia and Pannonia. The establishment of the Trpimirović dynasty ca. 850 brought strengthening to the Dalmatian Croat duchy, which became a kingdom in 925. In 1102 Croatia entered into a personal union with the Kingdom of Hungary. After the 1526 Battle of Mohács, the "Reliquiae reliquiarum olim inclyti Regni Croatiae" (the remains of the Kingdom of Croatia) became a part of the Habsburg Monarchy in 1527. In 1918 Croatia became a part of the Kingdom of SHS and later the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. In 1941-1945 during World War II, an Axis puppet state known as the Independent State of Croatia existed. After the victory of Tito's People's Liberation Movement and the Allies, Croatia became a constitutive federal republic of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. In 1991 Croatia proclaimed independence by holding the first democratic elections in the country but had to fight a long and bloody war against the Serb rebels and JNA until 1995. Croatia was recognized on January 15, 1992 by the European Union and the United Nations. The first country to recognize Croatia was Iceland on December 19, 1991. Government and politics Banski dvoriSince the adoption of the 1990 Constitution, Croatia has been a democratic republic. Between 1990 and 2000 it had a semi-presidential system, and since 2000 it has a parliamentary system. The President of the Republic (Predsjednik) is the head of state, directly elected to a five-year term and is limited by the Constitution to a maximum of two terms. In addition to being the commander in chief of the armed forces, the president has the procedural duty of appointing the Prime minister with the consent of the Parliament, and has some influence on foreign policy. His official residence is Predsjednički dvori. Apart from that he has summer residences on the islands of Vanga (Brijuni islands) and the island of Hvar. The Croatian Parliament (Sabor) is a unicameral legislative body (a second chamber, the "House of Counties", which was set up by the Constitution of 1990, was abolished in 2001). The number of the Sabor's members can vary from 100 to 160; they are all elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms. The plenary sessions of the Sabor take place from January 15 to July 15, and from September 15 to December 15. The Croatian Government (Vlada) is headed by the Prime minister who has two deputy prime ministers and fourteen ministers in charge of particular sectors of activity. The executive branch is responsible for proposing legislation and a budget, executing the laws, and guiding the foreign and internal policies of the republic. Government's official residence is at Banski dvori. Recently, Bianca Kunjasic was voted in parliament. Geography Map of CroatiaCroatia is located between South-Central Europe and Middle Europe. Its shape resembles that of a crescent or a horseshoe, which flanks its neighbours Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Montenegro. To the north lie Slovenia and Hungary; Italy lies across the Adriatic Sea. Its mainland territory is split in two non-contiguous parts by the short coastline of Bosnia and Herzegovina around Neum. Its terrain is diverse, including: plains, lakes and rolling hills in the continental north and northeast (Central Croatia and Slavonia, part of the Pannonian Basin); densely wooded mountains in Lika and Gorski Kotar, part of the Dinaric Alps; rocky coastlines on the Adriatic Sea (Istria, Northern Seacoast and Dalmatia). Phytogeographically, Croatia belongs to the Boreal Kingdom and is shared between the Central European and Illyrian provinces of the Circumboreal Region and the Adriatic province of the Mediterranean Region. According to the WWF, the territory of Croatia can be subdivided into three ecoregions: the Pannonian mixed forests, Dinaric Mountains mixed forests and Illyrian deciduous forests. The country is famous for its many national parks. Croatia has a mixture of climates. In the north and east it is continental, Mediterranean along the coast and a semi-highland and highland climate in the south-central region. Offshore Croatia consists of over one thousand islands varying in size. The largest islands in Croatia are Cres and Krk which are located in the Adriatic Sea. The Danube, the second longest river in Europe, runs through the city of Vukovar. Dinara, the eponym of the Dinaric Alps, is the highest peak of Croatia at 1831 metres above sea level. Counties The Plitvice Lakes, a UNESCO World Heritage SiteCroatia is divided into 20 counties (županija) and the capital Zagreb's city district (in italics below): Anglicized name Native name 1 Zagreb Zagrebačka 2 Krapina-Zagorje Krapinsko-zagorska 3 Sisak-Moslavina Sisačko-moslavačka 4 Karlovac Karlovačka 5 Varaždin Varaždinska 6 Koprivnica-Križevci Koprivničko-križevačka 7 Bjelovar-Bilogora Bjelovarsko-bilogorska 8 Primorje-Gorski Kotar Primorsko-goranska 9 Lika-Senj Ličko-senjska 10 Virovitica-Podravina Virovitičko-podravska 11 Požega-Slavonia Požeško-slavonska 12 Brod-Posavina Brodsko-posavska 13 Zadar Zadarska 14 Osijek-Baranja Osječko-baranjska 15 Šibenik-Knin Šibensko-kninska 16 Vukovar-Srijem Vukovarsko-srijemska 17 Split-Dalmatia Splitsko-dalmatinska 18 Istria Istarska 19 Dubrovnik-Neretva Dubrovačko-neretvanska 20 Međimurje Međimurska 21 City of Zagreb Grad Zagreb Demographics Croatia is inhabited mostly by Croats (89.9 per cent of the population). There are around twenty minority groups. Serbs are the largest minority, comprising 4.5 per cent of the total population. The predominant religion is Catholicism (87.8 per cent), with some Orthodox (4.4 per cent) and Sunni Muslim (1.3 per cent) minorities. The official and common language, Croatian, is a South Slavic language, using the Latin alphabet. According to the 2001 census, 96.1 per cent of the population speak Croatian as their first language. The population of Croatia has been stagnating over the last decade. During the 1991-1995 war, large sections of the population were displaced and emigration increasćed. In 1991 during an ethnic cleansing campaign carried out by rebel-Serb forces and the JNA under control of the former Serbian president Slobodan Milosevic 80,000 Croats were expelled from their homes by force. 11,834 Croats were killed and 1348 are still missing.Even moderate Serbs were killed by Serb forces.Many Croats have returned but a large portion fled to western Europe and stayed there.A large number of Croats (around 118,000)expelled from Serb-held parts of Bosnia,mostly Bosanska Posavina in 1992 continue to live in Croatia unable to return to their homes.Some 200,000 Serbs left Croatia at the end of the war.Only a minority of Serbs have returned to Croatia since 1995. The natural growth rate of the population is currently negative with the demographic transition completed half a century ago. Average life expectancy is 75.1 years, and the literacy rate is 98.1 per cent. Law Croatia has a three-tiered judicial system, consisting of the Supreme Court, County courts, and Municipal courts. The Constitutional Court rules on matters regarding the Constitution. Economy Dubrovnik's Old City, a UNESCO World Heritage Site and major tourist attractionThe Croatian economy has a stable functioning market economy which is one of the most advanced of South-Eastern Europe. International Monetary Fund data shows that Croatian nominal GDP stood at US$50.053 billion, or US$11,271 per capita, in 2007. The IMF forecast for 2008 is US$54.950 billion, or US$12,374 per capita. In purchasing power parity terms, total GDP was US$69.866 billion in 2007, equivalent to US$15,733 per capita. For 2008, it is forecast to be US$74.419 billion, or US$16,758 per capita. According to Eurostat data, Croatian PPS GDP per capita stood at 57.5 per cent of the EU average in 2007, and is forecast to reach 57.8 per cent in 2008. Real GDP growth in 2007 was 6.0 per cent. The average gross salary in 2007 was 6,634 kuna per month. In 2007, the International Labour Organization-defined unemployment rate stood at 9.1 per cent, after falling steadily from 14.7 percent in 2002. The registered unemployment rate is higher, though, standing at 14.7 percent in December 2007. In 2007, 7.2 percent of economic output was accounted for by agriculture, 32.8 percent by industry and 60.7 percent by the service sector. According to 2004 data, 2.7 percent of the workforce were employed in agriculture, 32.8 percent by industry and 64.5 in services. The industrial sector is dominated by shipbuilding, food processing and the chemical industry. Tourism is a notable source of income during the summer, with over 10 million foreign tourists in 2006 generating a revenue of €8 billion. Croatia is ranked as the 18th most popular tourist destination in the world. In 2006 Croatia exported goods to the value of USD$10.4 billion (FOB) (US$19.7 billion including service exports). Of particular concern is the backlogged judiciary system, combined with inefficient public administration, especially issues of land ownership and corruption. Another main problem includes the large and growing national debt which has reached over 30 billion dollars. The country has been preparing for membership in the European Union, its most important trading partner. In February 2005, the Stabilisation and Association Agreement with the EU officially came into force. Education Primary education in Croatia starts at the age of six or seven and consists of eight grades. Secondary education is provided by gymnasiums and vocational schools. Croatia has seven universities, the University of Zagreb, University of Split, University of Rijeka, University of Osijek, University of Zadar, University of Dubrovnik and the University of Pula. The University of Zagreb was founded in 1669 and is therefore the oldest in Southeastern Europe. There are also polytechnic higher education institutions. Transport Croatia has an extensive rail network, although due to historical circumstances, the Istria region is not accessible by train without passing through neighbouring Slovenia. Train services are operated by Croatian Railways (Croatian: Hrvatske željeznice). Major airports are located in Zagreb, Zadar, Split, Dubrovnik, Rijeka (on the island of Krk), Osijek, Bol, Lošinj and Pula. Croatia Airlines is the national airline and flag carrier. An extensive system of ferries, operated by Jadrolinija, serves Croatia's many islands and links coastal cities. Ferry services are also available to Italy. Culture Arena, the Roman amphitheatre in PulaCroatian culture is the result of a thirteen century-long history which has seen the development of many cities and monuments. The country includes six World Heritage sites and eight national parks. Croatia is also the birthplace of a number of historical figures included among the notable people are three Nobel prize winners, and numerous inventors. Some of the world's first fountain pens came from Croatia. Croatia also has a place in the history of clothing as the origin of the necktie (kravata). The country has a long artistic, literary and musical tradition. Also of interest is the diverse nature of Croatian cuisine. Properties inscribed on the World Heritage List Šibenik, The Cathedral of St James (St. Jacob) Cultural Episcopal Complex of the Euphrasian Basilica in the Historic Centre of Poreč (1997) Historic City of Trogir (1997) Historical Complex of Split with the Palace of Diocletian (1979) Old City of Dubrovnik (1979) The Cathedral of St James in Šibenik(2000) Natural Plitvice Lakes National Park (1979) Sport Sports popular in Croatia include football, handball, basketball, water polo and tennis. The Croatian national football team finished third in the 1998 FIFA World Cup and Davor Šuker won the Golden Boot as the top goal scorer. The country failed in its joint bid with Hungary to co-host the 2012 European Championships. The two main teams in Croatia are NK Dinamo Zagreb with between 33% and 36% of the population supporting them and HNK Hajduk Split with about 25%. Croatian national handball team were world champions in 2003 and two time Olympic winners in 1996 and 2004. Ivano Balić is considered to be the best handball player in the world. RK Zagreb was a two time European champion and RK Bjelovar won the same championship once. The national basketball team finished third at the 1994 FIBA World Championship, second at the 1992 Summer Olympics and third at EuroBasket 1993 and 1995. Croatian basketball clubs were European champions 5 times , KK Split three times and KK Cibona twice. The third most famous basketball club is KK Zadar. Croatian national water polo team are the current world champions. Mladost was a seven time European champion and was awarded the title Best Club of the 20th Century by LEN. Jug and Jadran were both three time European champions. Croatian Davis Cup team won the tournament in 2005. Tennis player Goran Ivanišević is one of the country's most recognisable sportsmen who won the 2001 Men's Singles title at Wimbledon. Janica Kostelić and Ivica Kostelić in skiing, Blanka Vlašić in athletics, Duje Draganja, Sanja Jovanović and Đurđica Bjedov in swimming, Dražen Petrović, Krešimir Ćosić, Toni Kukoč and Dino Rađa in basketball, Matija Ljubek in canoeing, Željko Mavrović and Mate Parlov in boxing, Branko Cikatić and Mirko Filipović, known as "Cro Cop", in kickboxing and mixed martial arts, Tamara Boroš in table tennis are among the most famous athletes. |
|