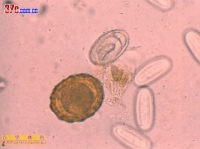
 美丽筒线虫 美丽筒线虫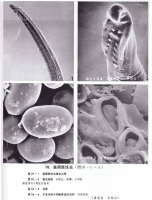 美丽筒线虫 美丽筒线虫![美麗筒線蟲_美麗筒線蟲的診斷_醫學百科 [返回]4 美麗筒線蟲的生活史
Click to view picture details](http://oson.ca/upload/images11/cache/1ac75cf899d08809c8f4563b92c2dde7.jpg) 美丽筒线虫 美丽筒线虫 美丽筒线虫 美丽筒线虫 美丽筒线虫 美丽筒线虫
Tube is in a total of 34 nematode species, which feed on rodents cancer tube worm (g.neoplasticum) and the East tube worm (g.orientale) are often thought to stimulate the parasitic parts, can cause cancer there. Have been found even in the human body is beautiful tube parasitic nematodes (g. pulchrum molin, 1857). baylis (1925) believe that cancer is a beautiful tube worm tube worm Common names. For the prevention of esophageal cancer, this issue should be studied further.
Beautiful tube worms and many ruminant pigs, monkeys, bears and other oral and esophageal mucosa and submucosa of the parasites. The earliest cases of human parasitism by leidy (1850) in Philadelphia and the pane (1864) were found in Italy. Since then another around the world have reported sporadic cases. Henan, China since 1955, found in 1 patient after the first, over a hundred cases have been reported so far, located in Shandong, Heilongjiang, Liaoning, Inner Mongolia, Gansu, Shaanxi, Qinghai, Sichuan, Beijing, Hebei, Tianjin, Henan, Shanxi, Shanghai, Jiangsu, Hubei, Hunan, Fujian, Guangdong and other 19 provinces (cities, districts), of which the most cases reported in Shandong,
Adult slender, white, parasitic on the body were smaller, in ruminant animals are larger. Parasites obtained from the human body, male length 21.5 ~ 62.0mm, width 0.1 ~ 0.3mm, female length 32 ~ 150mm, width 0.2 ~ 0.53mm,
Surface with thin stripes. Parasites preceding table rows leather significant cluster, size, number of different flower-like skin edge sudden, arranged in four rows in front, flank until nearly increased to 8 at the line. Mouth small, located in the central front, the sides of a leaf of the side lip, the lips on both sides of the back, ventral lip between each one. Male tail end of a clear membrane. Female tail blunt cone, asymmetric, slightly curved belly, uterus thick, containing a large number of eggs. Male tail with obvious tail, asymmetry, spicule 2, the length and shapes.
The cavity of the parasitic worms in the population sites were on the lower lip, cheek, tongue, hard palate, gums, tonsils, etc. nearby. Worms in the mucosa and submucosa can move freely, small blisters and parasitic parts appear white linear uplift. Patients with oral worm-like crawling, foreign body sensation or itching, may also have numbness, swelling, pain, rough mucosa, saliva increased, severe numbness in cheek tongue stiffness, limited mobility, affecting speech, hoarseness or difficulty swallowing and so on. If the lower esophageal mucosal parasite, can cause superficial mucosal ulcers, causing vomiting. Increase in eosinophils, peripheral white blood cell count can be accounted for 20%. The symptoms disappeared immediately after removing the worm.
According to oral symptoms and medical history may make the initial diagnosis to pin prick at the mucous membrane with parasite migration, remove the parasites for insect species identification is the basis for diagnosis of the disease.
Treatment of this disease is to prick out the parasitic worms mucosal site can also be applied to parts of the adult parasites Nu Fuka for solution, so that worms easily removed from the mucosa. Preventive measures to promote education, health diet, do not eat beetles and cockroaches, do not drink unboiled water and eating dirty lettuce.
Form
adults:
Male 25 × 0.2 mm, membranous tail tail
Female 52 × 0.3 mm, blunt tail cone.
With stripes across the body surface; the front of the vertical wavy skin penetration
Life history
adult parasites in cattle, sheep, horses, pigs, rabbits, mice and other animals or people (even) of the esophagus, pharynx, and oral mucosa. Eggs with their saliva, feces. Intermediate hosts such as beetles or cockroaches.
people with cystic infection is the result of eating the body of insects, or from drinking contaminated raw water with cystic body or food cause.
de sac larvae in the stomach, along the stomach or duodenal mucosa up to the esophagus, pharynx, and oral mucosa develop into adults.
life a year or so, adults do not usually lay eggs in the body.
Clinical manifestations
parasitic sites were: lower lip, cheek, tongue, hard palate, gums, tonsils around
parasitic parts appear milky white bubbles and curved linear uplift, parasites in the mucosal or submucosal move, change position, move fast
asymptomatic or mild. Common symptoms include mouth-like insects crawling, foreign body sensation, itching; lip, cheek, tongue, etc. numbness, swelling, pain. Rough mucosa, saliva wait.
Diagnosis and control
based on clinical manifestations (symptoms and medical history) the initial diagnosis; mucosal surface of the skin with a needle prick, remove the parasites to confirm the diagnosis.
treatment of mucosal surface of the skin with a needle prick, remove parasites, or novocaine coated surface of the skin to stimulate parts of the parasitic worms from the exit. Prognosis is good.
strengthen publicity and education, attention to food hygiene, eating beetles and cockroaches, do not drink unboiled water, do not eat dirty lettuce. |
|
|