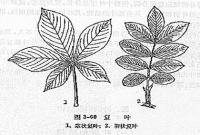
 完全叶 完全叶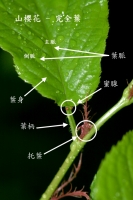 完全叶 完全叶
Broadly speaking, those who adapt to the structure of photosynthesis can be called a leaf, such as certain algae, mosses, or body of the "leaves" can be called the leaf; from the narrow sense, only vascular plants have real leaves. If the leaves of plants with leaves, petioles and stipular leaf called complete without stipules, or without stipules and petiole, called the incomplete leaf. For example, monocots, grasses and orchids in the leaf petiole and stipules not only sheath.
【Composition】
A typical leaf from leaf, petiole and stipule form. Leaf blade is the most important part, is generally flat, thin body, the characteristics and its physiological functions - to adapt photosynthesis. Distribution of the veins in the leaves, leaf veins stretching with the support and conduct water and nutrients to function. Petiole in the leaf base, and with the stem attached. Function is to support the leaf petioles and leaves arranged in a certain spatial location, to receive more sunlight and contact between the leaves and stems of water and transporting nutrients. Stipules at petiole and stem of the phase connections, usually small, caducous.
【Structure】
Angiosperm leaves tend to be more consistent with the structure, is composed of epidermis, mesophyll and the vein is composed of three parts. Epidermis is composed of a layer of living cells, but there are a few leaf epidermis is a multi-cell structure, called the multiple epidermis. Thick outer wall of epidermal cells, with cuticle, and some and waxy. Epidermal leaf surface is also often an adjunct - hair and stomatal (control). Contain many chloroplasts from the mesophyll parenchyma cells can carry out photosynthesis. General plant leaves was divided into palisade mesophyll and spongy. Vascular bundles in leaves called veins, veins on the leaves of the distribution form of the general points: stockwork and parallel veins. Vein is composed of vascular and mechanical tissues. Vascular stem and also the same, there are xylem and phloem, but also usually have between them form a layer, but the formation of the active layer is limited, produced only small amounts of secondary structure. Many plants have small veins with specialized absorption and transport function of transfer cells. Vascular veins are not in direct contact with the mesophyll cells, while separated bundle sheath. Photosynthetic carbon fixation in different ways c3, c4 plants, and their bundle sheath structure is different.
【Category】
〖〗 Large leaf and small leaf
By the system development point of view, leaves can be divided into small leaves and large leaves. Different types of leaf size and shape are very different. The length of leaves, small only a few millimeters, large up to a few meters. Greater changes in leaf shape. Leaves leaf margin, leaf tip, leaf base and the distribution of the vein, each plant is different.
〗 〖Single leaf and compound leaf
Each leaf blade is called only one single leaf, petiole on the leaf blade of two or more called fronds. Compound leaves arranged in different ways by leaflets can be divided into pinnate and palmate fronds.
】 【Variation
According to the relationship between plants and water, the plant is divided into xeric plants, the plants and aquatic plants, which leaves the biggest changes. For example, xeric plants, Ye and thick or more hairs, epidermal cell wall thickness, cuticle development; some stomatal complex subsidence within the epidermis (oleander); otherwise xerophytic succulent, juicy leaves of hypertrophy, leaves have developed parenchyma, storage of large amounts of water.
In addition to the leaves of some plants adapt to the environment occurred metamorphosis, and some all the leaves into spines to reduce water loss, to adapt to living in arid environments (cactus); some stipular thorns into a hard, play a protective role (acacia); pea compound leaf tendrils into the top few slices of leaflets, climbing in the other objects. Insect-catching leaves of insectivorous plants to feed worms.
Life】 【leaves
Usually leaves bud has been formed, its development began in the stem end of leaf primordia growth cone. The beginning of leaf primordia formation, all of its cells also are the original meristem state. During development, cells gradually transition to the primary meristem. Leaves the primary meristem, and also roots, stems, like the original into the epidermis, the ground meristem and procambium. In the young leaf is no longer retain the original meristem, so the whole young leaves during development of all mature, unlike roots and stems retained apical meristem. Leaf growth period is limited to a certain size in a short time, the growth stopped, but some plants in the leaf base retaining intermediate meristem, can have a longer growth period.
Growth is not the long leaves in plants, but on a certain life. General annuals, with leaves as the plants died. Perennial herbs and deciduous woody plants, the leaf life span of only one growing season. Evergreen woody plants, leaf life span may have a few years. Perennial herbs and woody plants, which produce leaves and the separation after the leaves to fall off from here. Separation not only from the petiole, can also be generated in the stalks and stems, easy to flower and fruit shedding. |